How To Solve A Truss Method Of Sections
For planar two dimensional trusses we have three equilibrium equations we can use for any section of the truss.
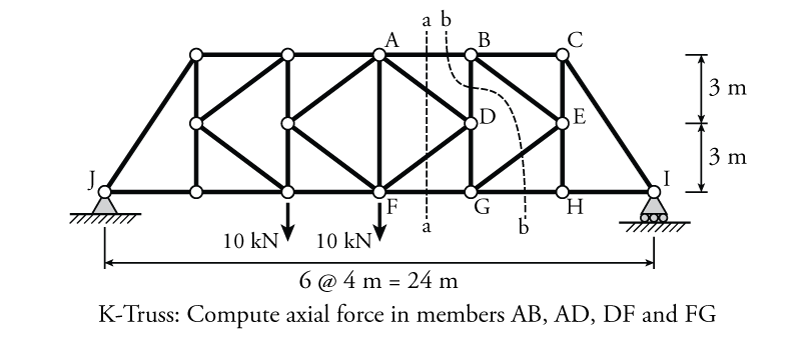
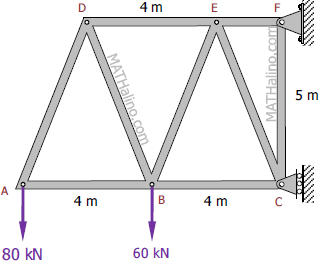
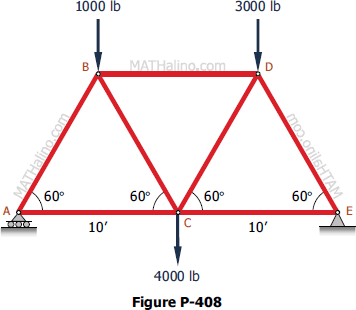
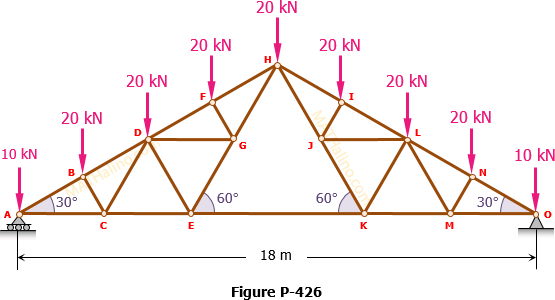
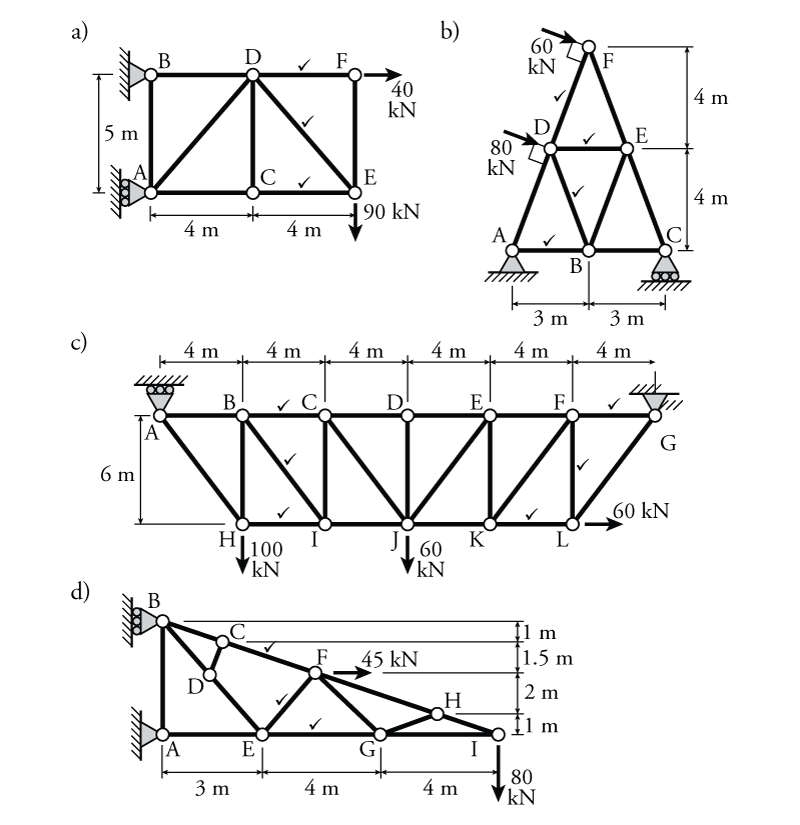
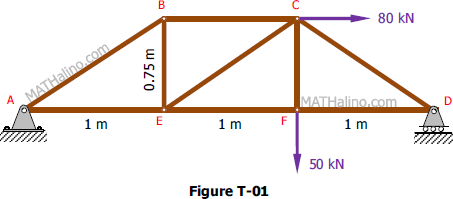
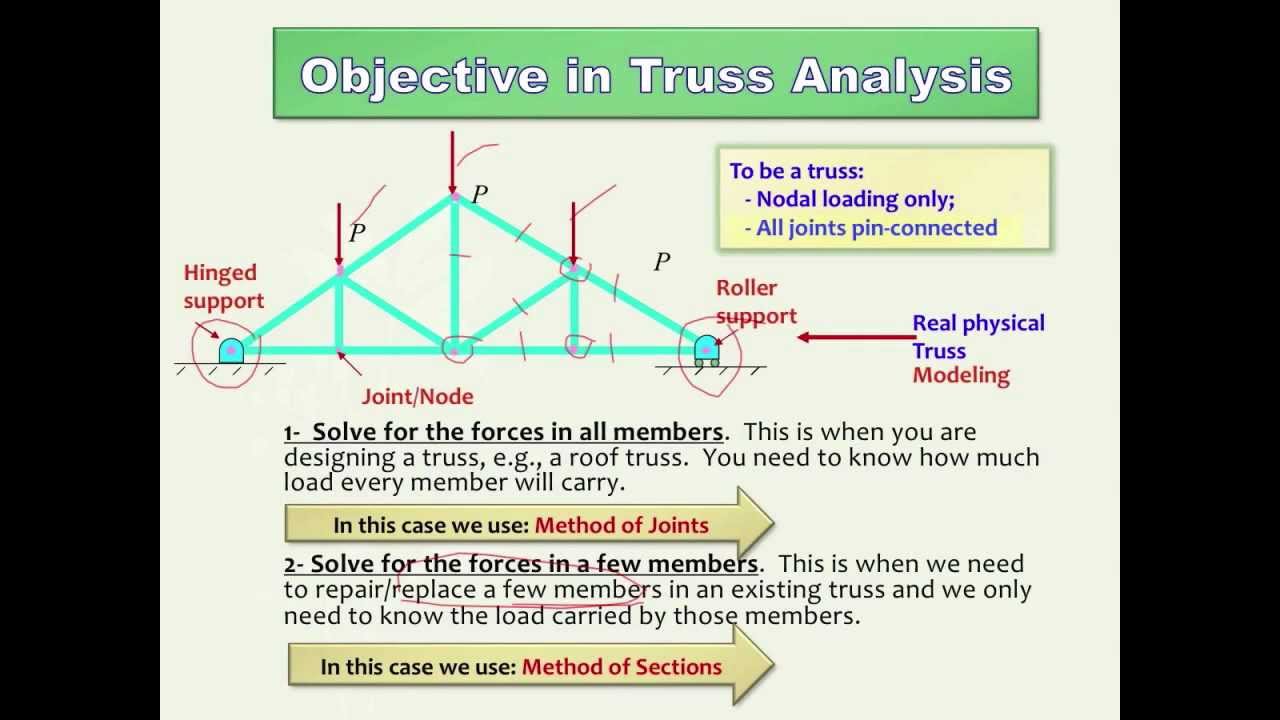
How to solve a truss method of sections. This method permits us to solve directly any member by analyzing the left or the right section of the cutting plane. Like most static structural analysis we must first start by locating. The first step is to draw the free body diagram for the given truss.
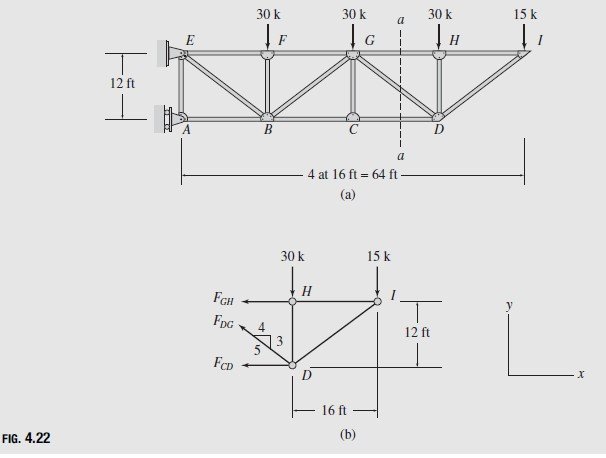
How to solve truss problems using method of sections step by step step 1. This demonstration solves a truss using the method of sections which involves cutting along several selected members and taking the sum of the forces forces and moment about a pointselect solve for reaction forces to see how the reaction forces and are calculated use buttons to calculate the moment about do a force balance and see the solved forces when calculate moment is selected move the mouse. The method of sections is usually the fastest and easiest way to determine the unknown forces acting in a specific member.
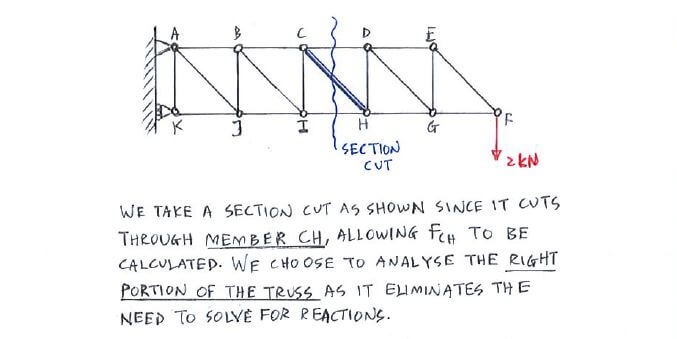
In this method we will cut the truss into two sections by passing a cutting plane through the members whose internal forces we wish to determine. Tutorial to solve truss by method of sections tutorial. The method involves breaking the truss down into individual sections and analyzing each section as a separate rigid body.
If the entire truss is in equilibrium every section of the truss must also be in equilibrium. The next step is to draw a free body of one part or the other indicating all known and unknown forces. The method of sections is a process used to solve for the unknown forces acting on members of a truss.
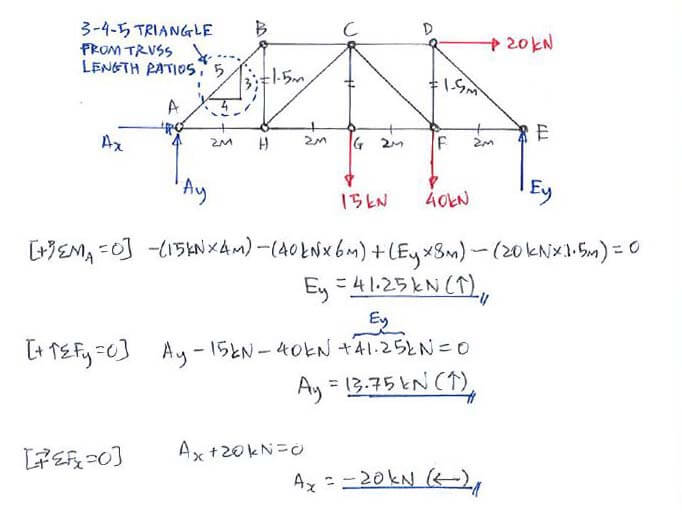
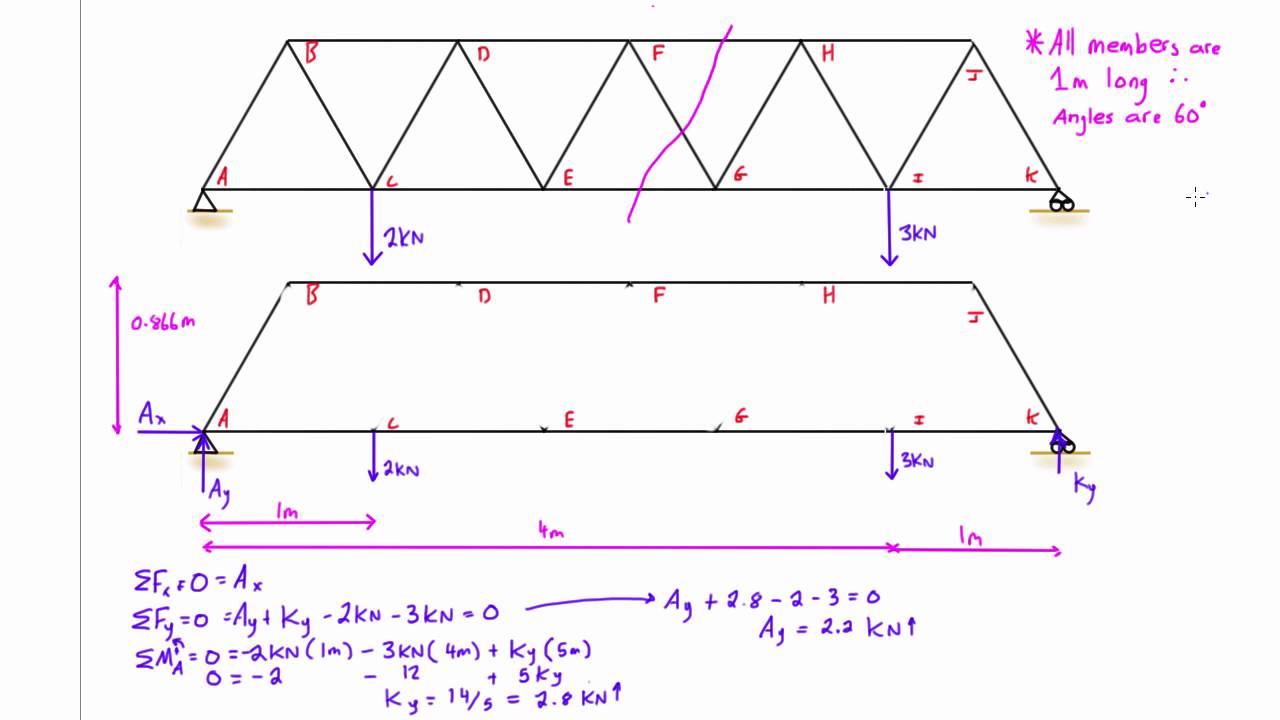
Checking for determinacy or indeterminacy. Calculate the reactions at the supports. Drawing of free body diagram.
To remain each section in equilibrium the cut members will be replaced by forces equivalent to the internal load transmitted to the members. To solve this problem by the method of sections you pass a section indicated by a line through three members of the truss one of which is the desired member. In this tutorial we will explore and learn the.