Principle Of Frozen Section

I would like to discuss what i consider the limitations in frozen section.
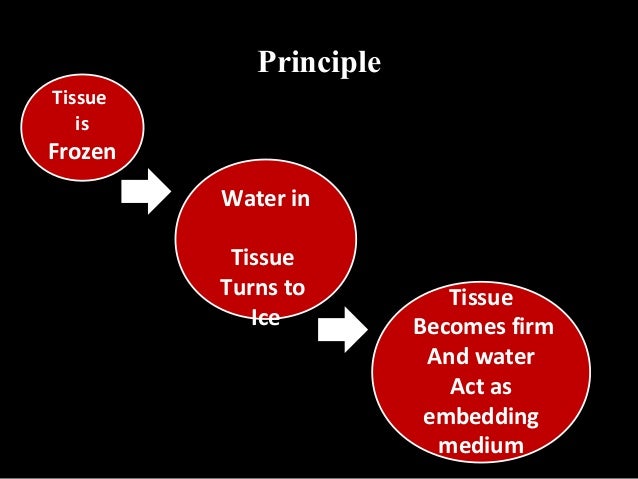
Principle of frozen section. The frozen section process is very demanding by virtue of the ever present pressure to provide a fast result. The principle of frozen section when the tissue sample goes through rapid freezing it converts water into ice which acts as an embedding media allowing the tissue to be sectioned. 2 gently lift up while crossing the blade as the brush and block meet the blade the section will begin to form under the brush.
Wilson frozen section resulted from need for rapid intra operative diagnosis. After years of research i find this to be exactly in between too cold and too warm. There is an ideal temperature for cutting the frozen section block.
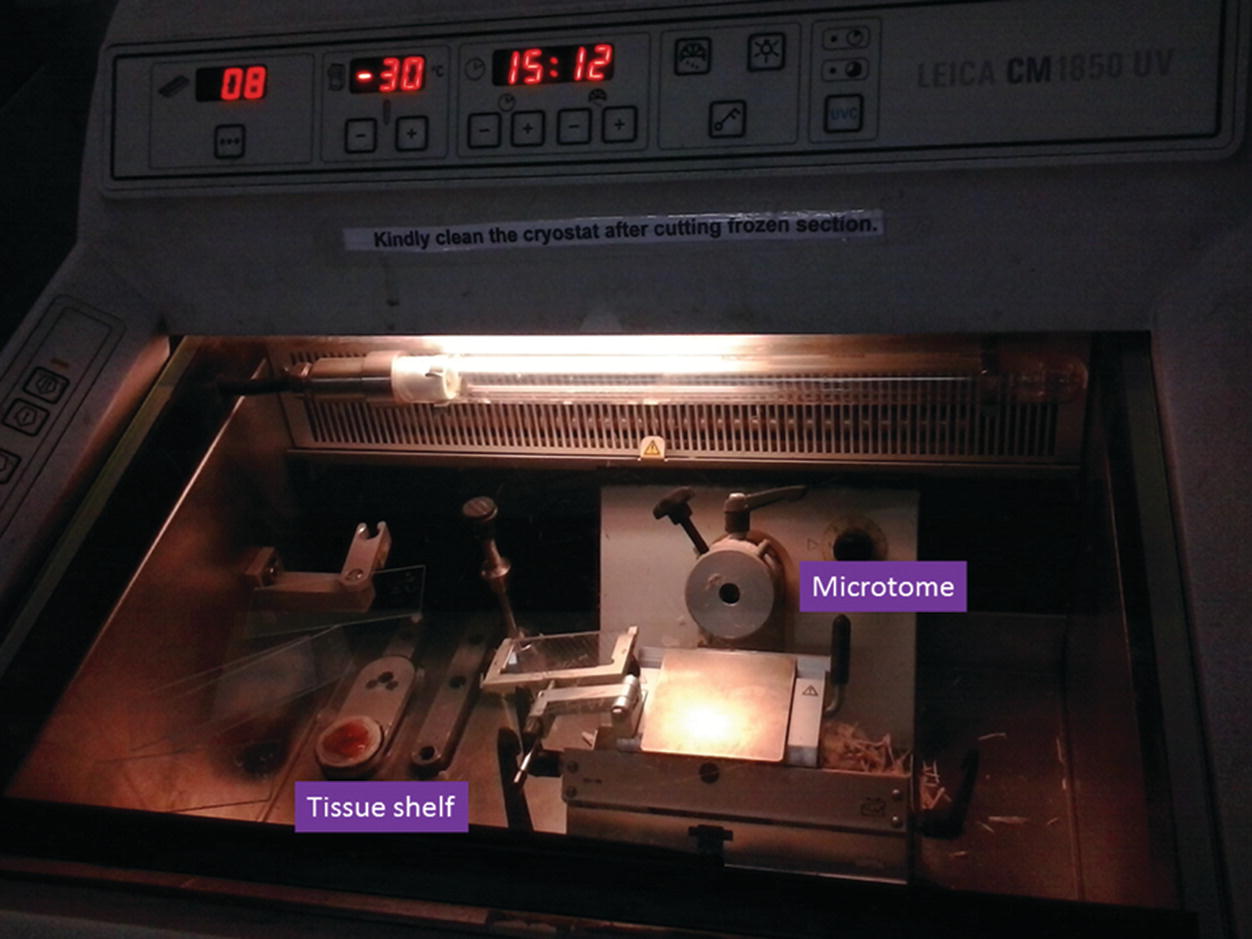
Give the details as much required do not give unnecessary detail or explaination. The cryostat is the instrument to freeze the tissue and also to cut the frozen tissue for microscopic section. 1 ride the block as the block descends toward the brush the brush keeps pace with the block by gently resting on the bottom 2 3 mm of the block.
The cryostat is the instrument to freeze the tissue. The rapid freezing of the tissue sample converts the water into ice. The manual of surgical pathology 2 in a section titled frozen sections are not permanent sections points to four reasons.
The frozen section procedure is a pathological laboratory procedure to perform rapid microscopic analysis of a specimen. The frozen section is the rapid tissue section by cooling the tissue with the help of cryostat to provide immediate report of the tissue sample. The stress is increased when multiple specimens are delivered by a number of surgeons simultaneously.
The technical name for this procedure is cryosection. I will divide these into two categories. Some important factors to note are.